Alfa Romeo

Turin, Piedmont, Italy
About
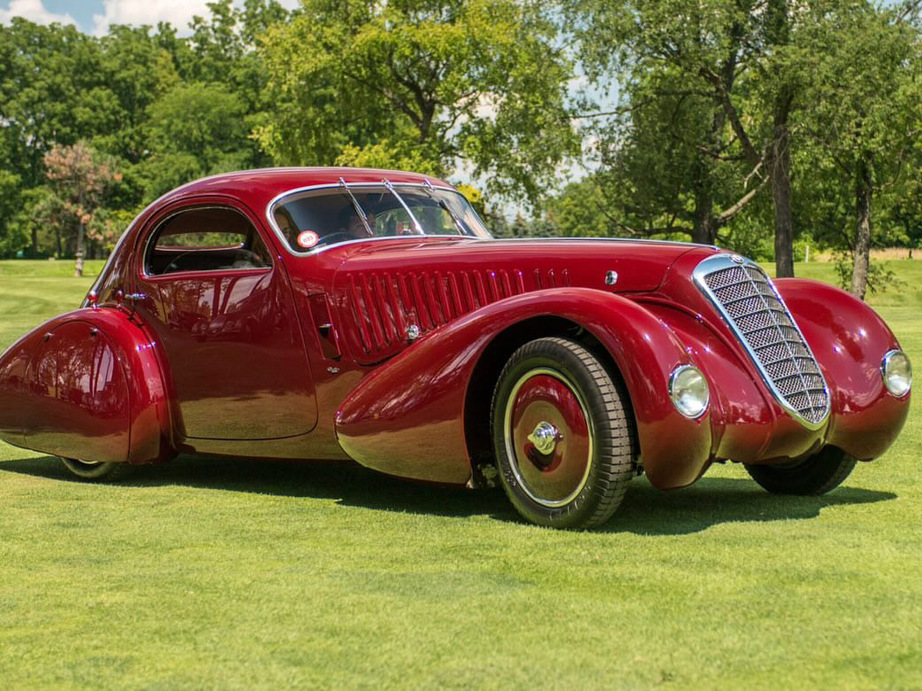
One of Italy's most iconic sporting car brands, Alfa Romeo traces its roots back to 1906 and the Società Italiana Automobili Darracq. Licensed to Ugo Stella from Darracq, the company produced cars in Naples and Milan before closing in 1910 after years of financial issues.
On 24 June that year, Stella and a group of investors launched Anonima Lombarda Fabbrica Automobili (A.L.F.A.), wanting to produce cars tailored to the Italian market. Engineer Giuseppe Merosi was hired shortly thereafter, culminating in the 24 HP and 12 HP models, more successful than the license-built Darracqs of yesteryear.
A.L.F.A. entered motor racing for the first time in 1911 and, despite some success, was still struggling financially. At the onset of the First World War, failure to obtain government contracts left A.L.F.A. in hot water, until the liquidating Bancia Italiana di Sconto agreed to allow engineer Nicola Romeo to use the company to fulfil his military contracts under his management. This accelerated A.L.F.A.'s growth, resulting in the investors making the company public in 1918 as 'Società Anonima Italiana Nicola Romeo & C.'.
At the war's end, Romeo decided to transition the company's return to civilian car production, under the prestigious moniker 'Alfa Romeo'. These exotic cars were priced out of the range of the Italian market, and business deteriorated. In 1921, Alfa helped pull the Banca Italiana di Sconto into bankruptcy, following which, both the BIC and, in turn, Alfa Romeo became part-owned by the Italian state.
Only the company's sporting victories prevented Mussolini from calling for closure, and Romeo was ousted in 1925. The tightrope of insolvency was walked for a decade, illuminated by the light of racing success until the Great Depression called for the government to assume complete control of the company. Restructuring, Ugo Gobbato was appointed as Managing Director and tapped into Alfa Romeo's potential.
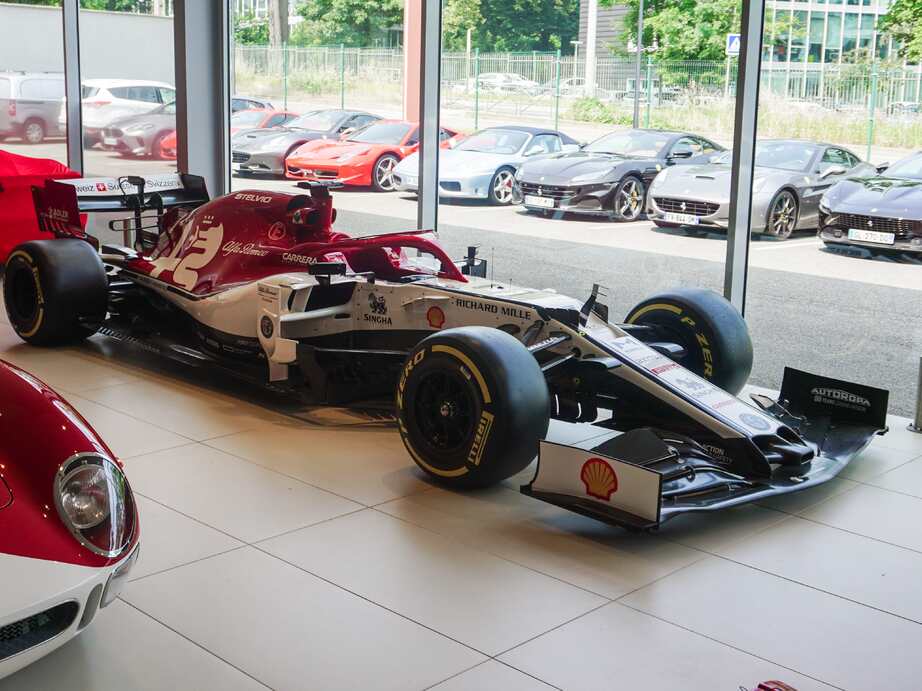
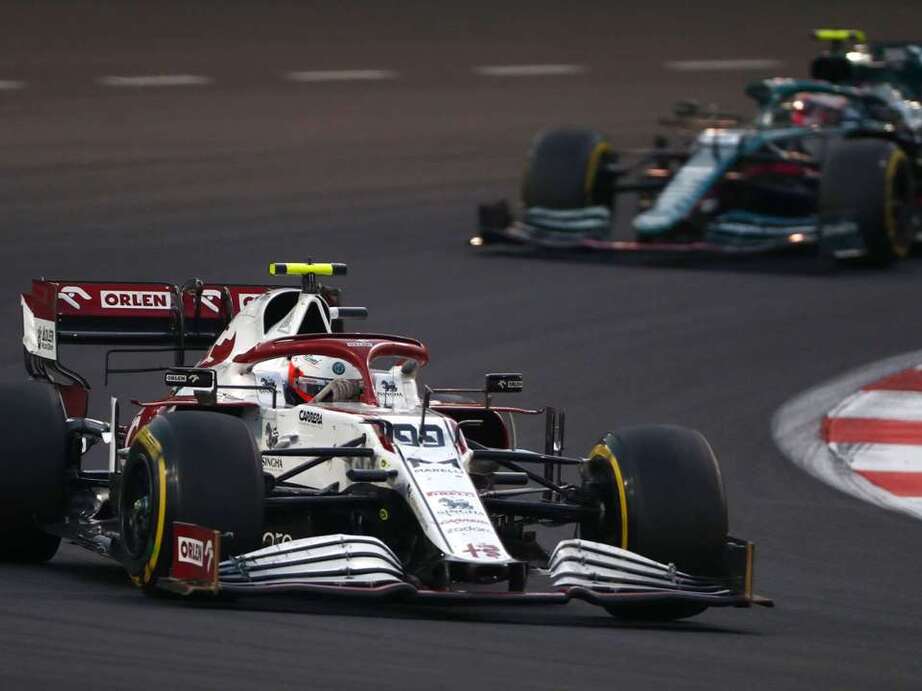
Producing cars, aero engines and commercial vehicles, Alfa Romeo became an industrial giant. They returned to racing under the eye of Enzo Ferrari in 1938, until war broke out again and munitions production became the focal point.
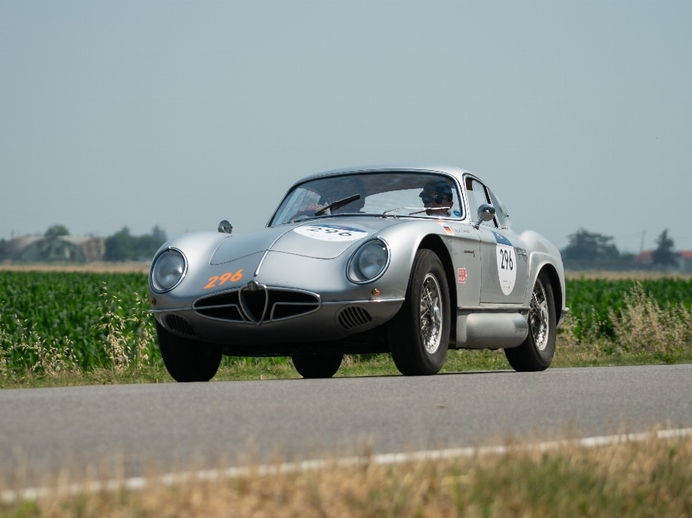
Struggling out of the conflict with a damaged factory and shortage of men and materials, Alfa Romeo slowly returned to car production, albeit with an 'everyman' approach necessitated by the harsh economic climate in post-war Europe. This continued into the '60s, when the Giulia and Giulietta models brought unprecedented growth for the company, both on the road and race track. Alfa Romeo became a household name for cars with a sporting edge and excelled in the American market in particular.
In 1986, following a period of quality, labour and social issues, the Italian government sold Alfa Romeo to Fiat. They nursed the company through their 2012 merger with Chrysler and continue to this day, under Stellantis.
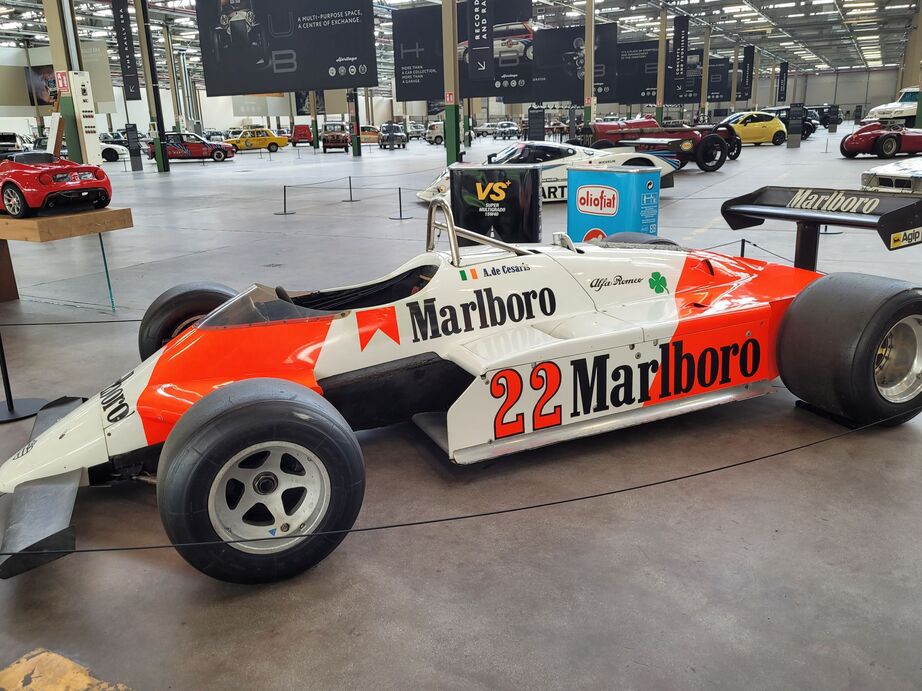
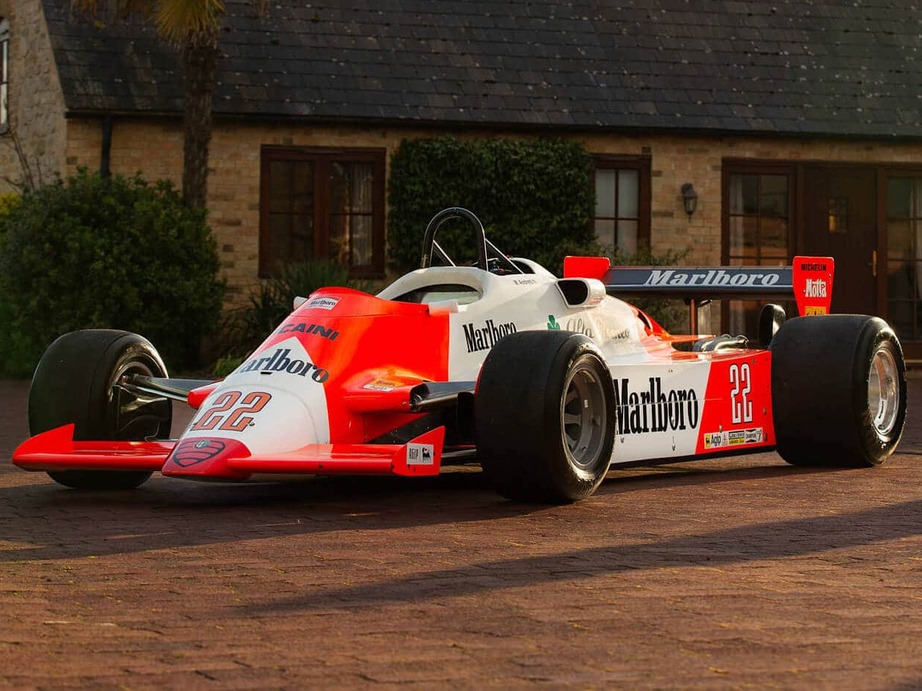
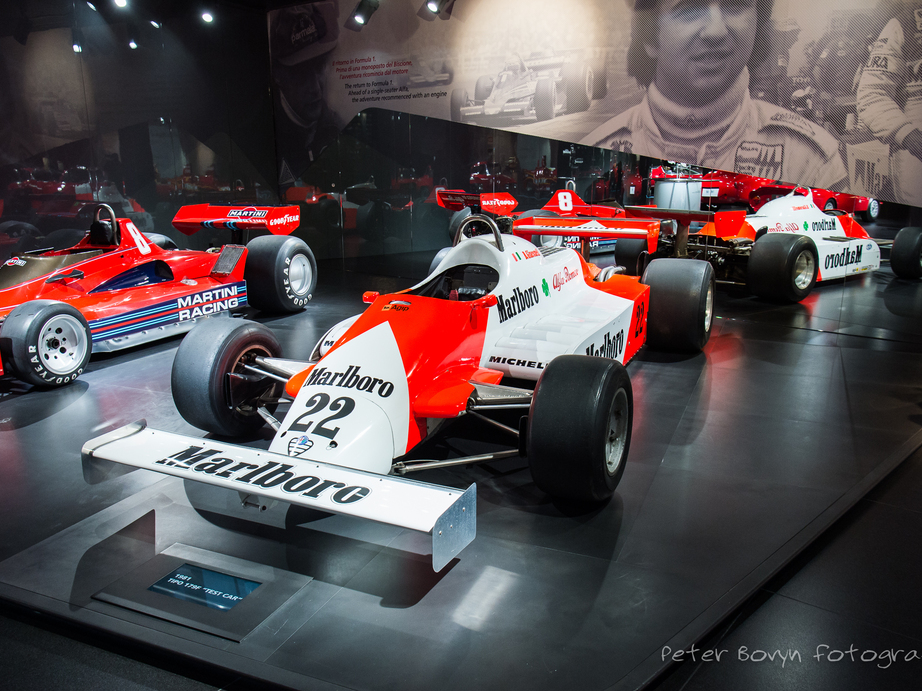
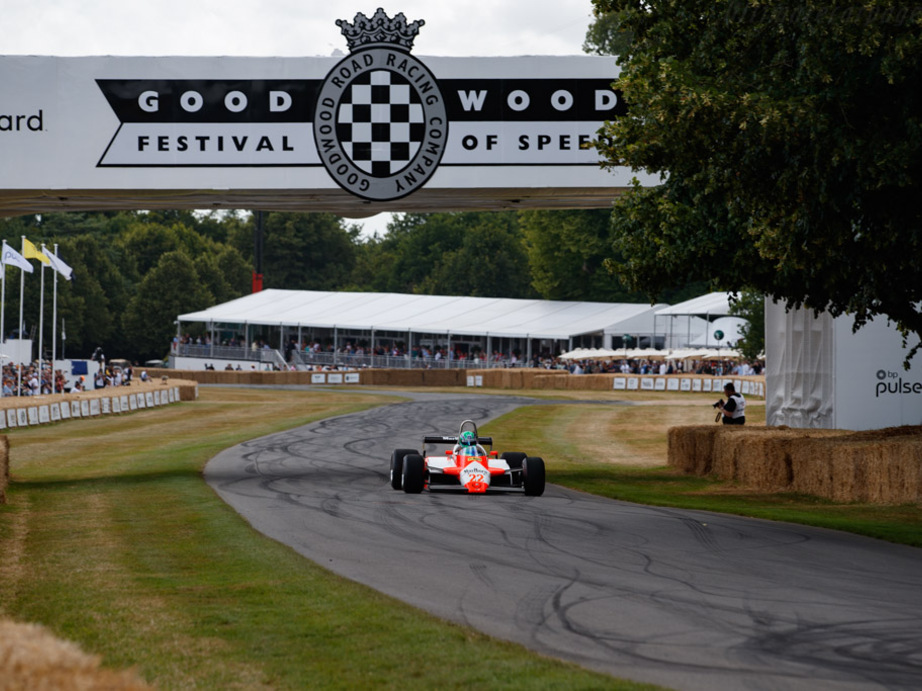















































































































Videos
Empty List
Gallery
No images available.












